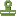
 Types of Diving Suits Types of Diving Suits
Underwater, we can easily suffer heat loss, so to prevent this heat loss it is important to wear a diving suit. Thus the principal aims of a diving suit are heat retention, body protection and buoyancy. So please choose your diving suit according to the expected water temperature.
|
|
|
① Drysuit
② Two-piece
③ One-piece
④ Skin suit |
|
Low-
temperature
water |
 |
High-
temperature
water |
|
Diving Suit Type and Water Temperature |
|
|
|
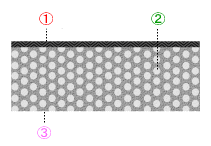
■Wetsuits
Made from neoprene, inside are a great number of air bubbles that retain heat while providing more buoyancy than rubber. Order-made neoprene wetsuits provide the maximum amount of heat retention by fitting your body perfectly.
|
① Jersey surface
② Air bubble |
 |
|
③ Skin surface |
|
 |
 |
Two-piece |
One-piece |
|
|
 |
 |
Seagull |
Two-sided skin |
|
|
|
■Drysuits
Since drysuits provide a barrier between your skin and the water, drysuits offer the highest heat retention of diving suits. Derived from neoprene or nylon, they offer motility and comfort while inlet and exhaust valves (located on the legs) allow for fine control.
|
 |
 |
Nylon-type |
Neoprene-type |
|
|
|
■Hood
Since In water we lose over 50% of our body heat from head and neck areas, in cool or cold water we need to use a hood. If we wear a vest with attached hood, we magnify our heat retention ability greatly. |
 |
 |
Hood |
Vest with Attached Hood |
|
|
|
|

